Basics
5 minute read
What is a pluscloud open Environment?
Each pluscloud open environment is designed as a “shared nothing” infrastructure, meaning that each environment is completely independent and does not share any underlying resources or management capabilities with other environments. While this may limit some flexibility in terms of workload placement and management, it enables true geo-redundancy concepts to be implemented by facilitating the isolation of resources and reducing the risk of correlated failures. The management layer within the environment which provides the API endpoints is high-available, ensuring that management operations remain available even in the event of infrastructure failures.
Public pluscloud open environments
| Region | Availability Zone | Internal Name | Horizon/UI Endpoint | Keystone Endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE-WEST | DE-WEST-1 | prod1 | https://prod1.api.pco.get-cloud.io | https://prod1.api.pco.get-cloud.io:5000 |
| DE-NORTH | DE-NORTH-1 | prod2 | https://prod2.api.pco.get-cloud.io | https://prod2.api.pco.get-cloud.io:5000 |
| DE-NORTH | DE-NORTH-2 | prod3 | https://prod3.api.pco.get-cloud.io | https://prod3.api.pco.get-cloud.io:5000 |
| DE-WEST | DE-WEST-2 | prod4 | https://prod4.api.pco.get-cloud.io | https://prod4.api.pco.get-cloud.io:5000 |
| DE-WEST | DE-WEST-2 | scs1 | https://ui.gx-scs.sovereignit.cloud | https://api.gx-scs.sovereignit.cloud:5000 |
| DE-WEST | DE-WEST-1 | scs2 | https://scs2.api.pco.get-cloud.io | https://scs2.api.pco.get-cloud.io:5000 |
Note
scs1 (deprecated) and scs2 are development environments provided exclusively in the context of Sovereign Cloud Stack & Gaia-X.Access
There are various options to work with pluscloud open environments. You can interact with the web UI (Horizon) or with the API.
Credentials
To login through Horizon, you will need the credentials we provided:
- Username
- Password
- Domain
Credentials for CLI Tools
The login data for various CLI tools such as the Openstack CLI, Terraform, OpenTofu or Ansible can be downloaded from Horizon.
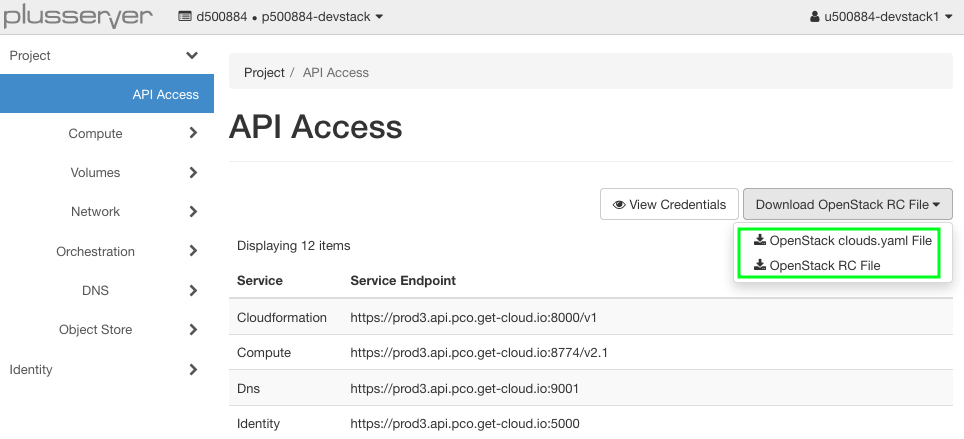
clouds.yaml
Most tools now prefer the clouds.yaml file, which can be split according to preference.
Authentication for the OpenStackClient is configured via files in YAML format. clouds.yml, clouds-public.yml and secure.yml are used to collect the credentials and authentication endpoints of one ore more OpenStack clouds (or pluscloud open Regions) you want to connect to.
Most tools expect these files in certain directories
- Current working directory
- ${HOME}/.config/openstack/
- /etc/openstack/
The repository of the SovereignCloudStack (SCS) has two templates for clouds-public.yml and clouds.yml.
Using clouds.yml and clouds-public.yml, you can specify more than one cloud to log in to and select the desired cloud with the parameter --os-cloud= or the environment variable OS_CLOUD when using the OpenStackClient.
RC File
Another option is to download an OpenRC environment file from the Horizon web interface. While logged into Horizon you click on “<your login name>” in the upper right corner and choose “OpenStack RC File” from the dropdown menu.
Then set the environment variables contained in the file as follows:
source ./<your_project_name>-openrc.sh
Please enter your OpenStack Password for project <your_project_name> as user <your username>:
Tools
OpenStack CLI
There are several options for you to install the OpenStackClient in your environment. Most Linux distributions offer the installation from their package repository (for distributions based on the Debian package management system, you can install the package via apt install python-openstackclient).
Since the OpenStackClient is written in the Python programming language, it can be installed via the Python Packaging System (pip install python-openstackclient). We would recommend to do this in a Python virtual environment (venv) in order to keep this installation seperated from the Python, that might be installed by your Linux distribution.
A Python venv can be created by executing python -m venv openstackclient. Change into the subdirectory and “activate” the virtual environment cd openstackclient ; . ./bin/activate. All installation of Python packages using pip install will now take place in the new venv. You can deactivate the venv by executing deactivate.
The third option is to use a Docker container, which includes all the required OpenStackclient bits. We recommend to use the openstackclient image from OSISM. You can pull this container if you have a local Docker or Podman installation on your workstation by executing docker pull quay.io/osism/openstackclient or podman pull quay.io/osism/openstackclient respectively.
For information on the OpenStackClient and its installation please see the upstream documentation upstream documentation.
Terraform provider and Packer builder
The Terraform provider for OpenStack can be found on the Terraform Registry website at https://registry.terraform.io/providers/terraform-provider-openstack/openstack/latest/docs.
This provider enables users to interact with many OpenStack resources. With the Terraform provider for OpenStack, users can create, modify, and delete pluscloud open resources through Terraform configuration files, allowing streamlined infrastructure management.
Furthermore, there is an OpenStack builder for packer, which allows users to create custom images on OpenStack.
Ansible Collections
Ansible is a popular automation tool that can be used to configure and manage infrastructure. Ansible provides a collection called openstack.cloud which includes a set of Ansible modules to interact with pluscloud open resources. These modules can be used to create, update, delete, and query resources such as virtual machines, networks, security groups, and more.
The openstack.cloud collection is available on the official Ansible website at https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/collections/openstack/index.html.
Maintenance
Platform Maintenance
A platform update/maintenance is always announced in advance and includes all Openstack components. This usually has no impact on your workload (VMs, Kubernetes clusters, …). “Only” the APIs are affected because the underlying services have to be restarted. This maintenance work usually takes place once every six months.
Hypervisor Maintenance
Each hypervisor must be updated and restarted at regular intervals. This is usually the case once a month.
Scheduled maintenance windows usually take place every day after 22:00 CEST. A normal restart of the hypervisor takes about 15 minutes, but can take longer in exceptional cases.
Before a hypervisor is restarted, we try to migrate all VMs live to another one so that there is no impact on the VMs. However, there is a metadata key called ps_automatic_maintenance that informs you when the migration will take place and you can decide whether or not to take action before the migration. However, most applications have no problems with live migration.
However, there are exceptions!
For several Flavors and Server Groups, we cannot migrate the VMs live. In this case, we will shut down the VMs for the duration of the hypervisor restart.
For more information on the exceptions, see the Maintenance details.