PSKE - Cluster provisioning
2 minute read
Via WebUI
In the menu “Clusters” (1), select the plus sign (2) for “Kubernetes Clusters”. The cluster creation form appears.
In the “Infrastructure” section, our pluscloud open is already selected for you. In the next step (1), you provide details about the cluster, such as the cluster name, the Kubernetes version, and the purpose of the cluster you are going to create. You can choose the predefined (random) cluster name, or you can choose your own more descriptive name:

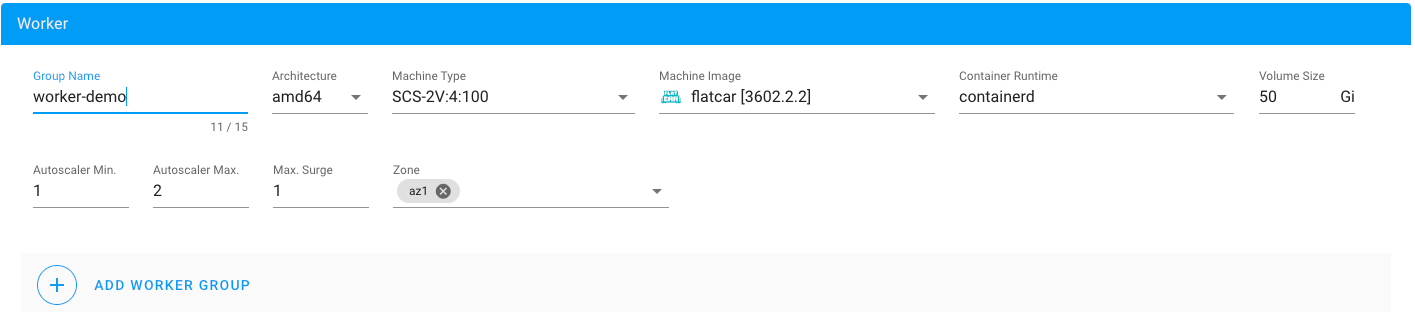
You can choose the size and number of worker nodes you want to create in the “Worker” section. The master/control plane nodes are not configurable by you because they are managed by Gardener.
The following example creates two worker nodes with the flavor “SCS-4V:8:100” (4 vCPUs, 8 GB RAM, 100 GB local storage). Ubuntu 20.04 is used as the operating system and containerd as the container runtime.
In the “Maintenance” section, you can select when the cluster should be checked for updates to the worker operating system and Kubernetes version, and updated if necessary. Updates can be controlled for automatic application using the “Auto Update” option.
The final section, “Hibernation,” defines when your cluster will automatically shut down and when the resources of the worker nodes will be removed at specific times. This is useful if you want to minimize costs with your cloud provider, for example, if you have a development cluster that does not need to be active all the time. You can specify one or more time windows.
The cluster is created with a final click on “Create”.
Via YAML
Clusters can be modified and created via the YAML section in the web interface, as a general Kubernetes-CRD or used by Terraform.
Here you can define for example the IP networks of the worker nodes, which must not overlap with the IP networks.
spec:
provider:
type: openstack
infrastructureConfig:
networks:
workers: 10.250.0.0/16
networking:
nodes: 10.250.0.0/16
Read more: Shoot Spec (via Cluster YAML)
Warning
The following overlaps must be avoided: 10.20.0.0/16, 10.64.0.0/12, 10.80.0.0/12, 192.168.123.0/24
Read more: Cluster Networking
This selection can be important if you later want to connect your Kubernetes cluster to an existing environment via the HybridConnector or Virtual Cloud Firewall.
Warning
It’s essential to ensure there are no network conflicts between your existing environment and the Kubernetes clusters itself.
Read more: HC - Provisioning & Cluster Networking