Setting Up the S3 Portal
4 minute read
In this section, we will guide you on creating a default group and assigning permissions for the plusserver S3 web interface. This allows users in this group to access all buckets.
Note that the security recommendation is to create a new user to replace the root user. The root user should only be used in emergencies.
Step 1: Logging in to the plusserver S3 Web Interface
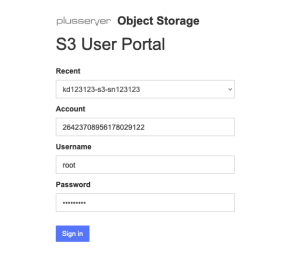
Open your web browser and visit the following website: https://s3-portal.psmanaged.com:9443/
Use the provided user credentials (you can find them in the plusserver customer portal: https://customerservice.plusserver.com/ under “Contracts and Billing” → Select S3 contract → Access data → “Show credentials”) to log in. The username is “root,” and use the password you are familiar with. You will also find the Account ID here.
Step 2: Creating a Default Group
- After successful login, click on “Access Management” on the left and select “Groups.”
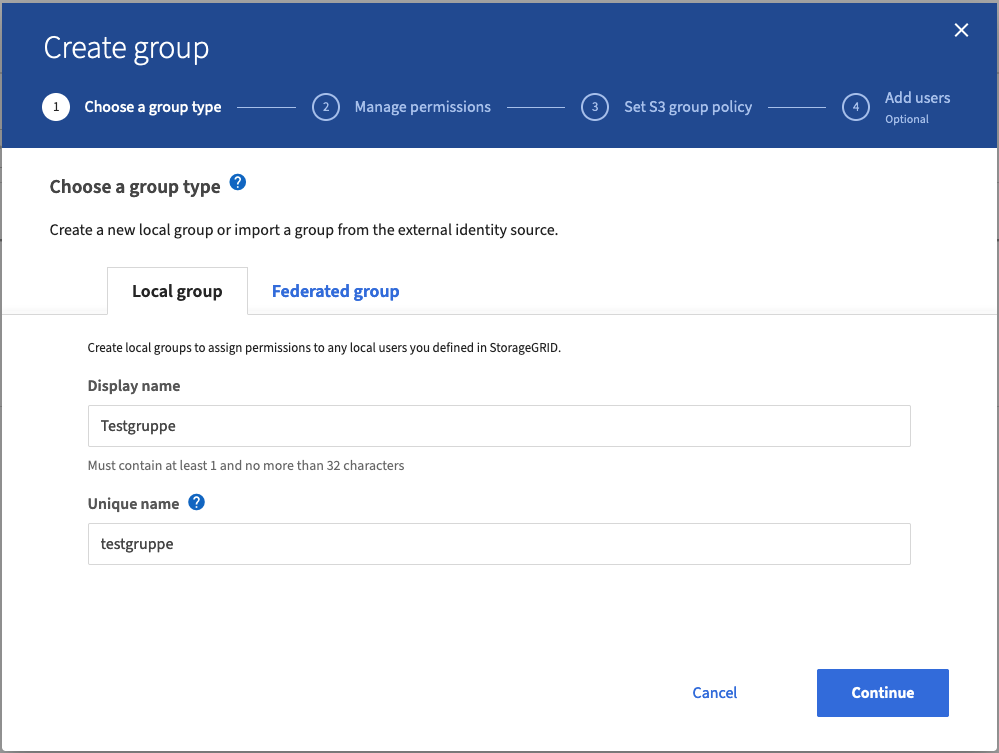
- Choose the option “Create Group” to create a new group.
- Enter a display name and a unique name for the group.
Step 3: Setting Permissions for the Group
- In the group settings, you can set the permissions for the users in this group. Please note that these permissions are specific to the plusserver S3 web interface.
- Assign the group the necessary permissions to access the desired actions and resources. Here, you can adjust the permissions based on your requirements.
Warning
Please be cautious when setting permissions and ensure that users only receive the necessary rights to ensure the security of your data.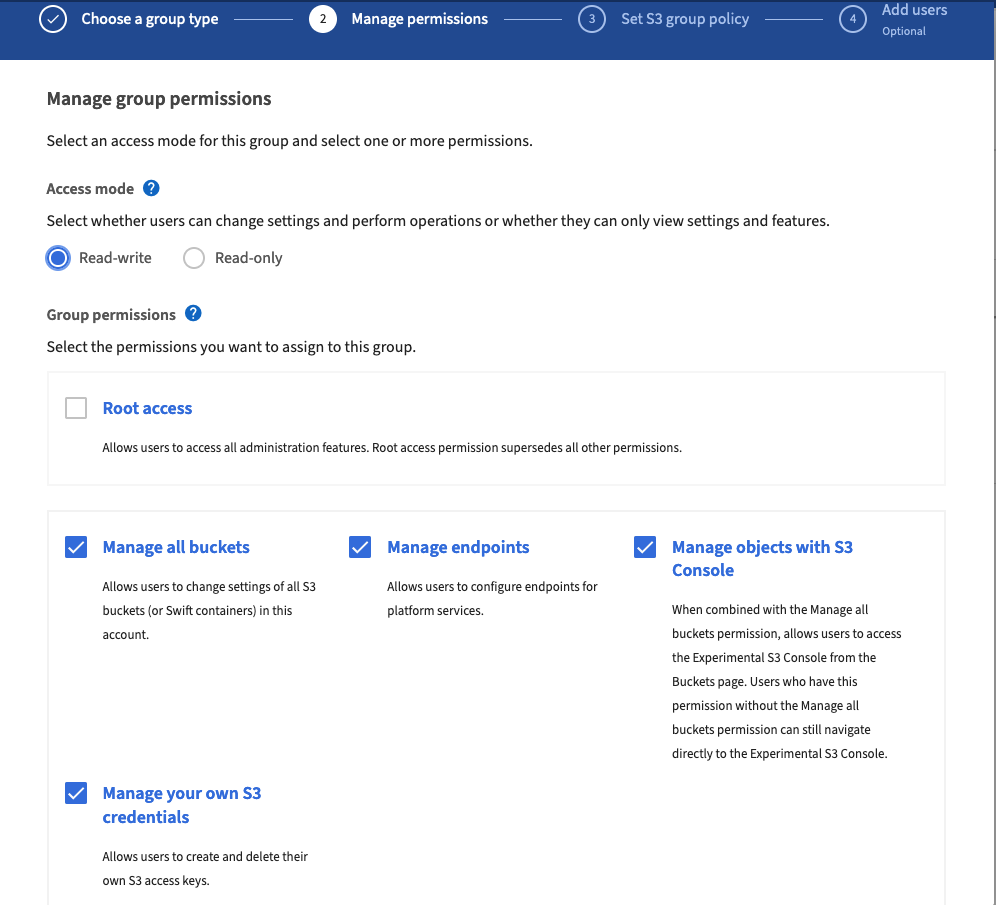
Step 4: Applying Group Permissions for the S3 Interface
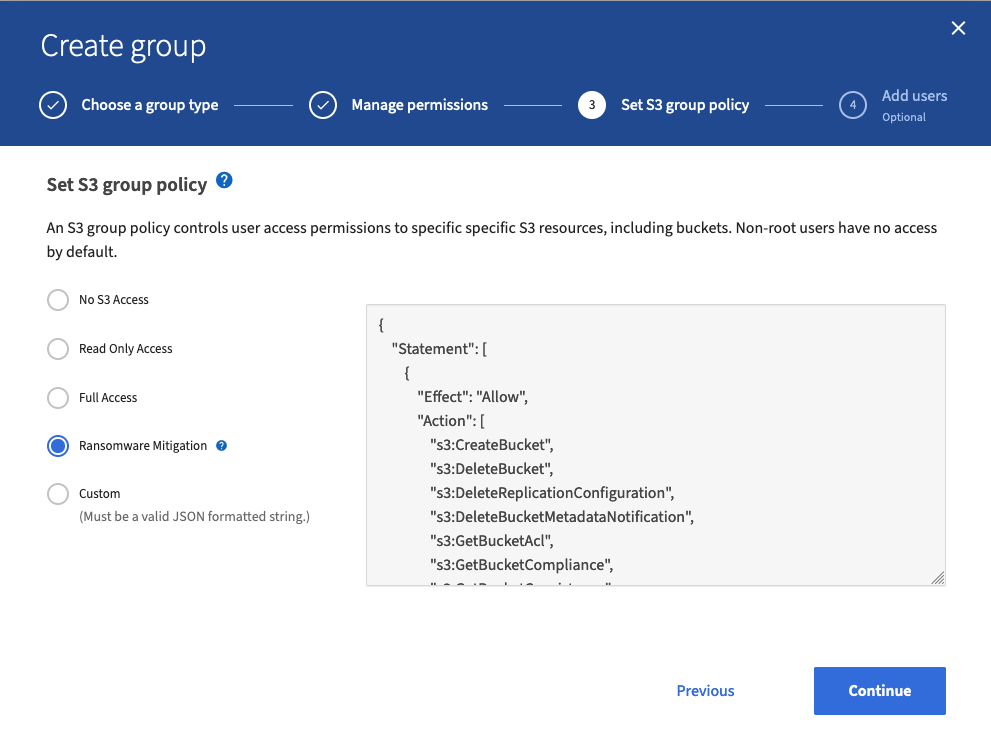
- In this example, we are using the “Ransomware Mitigation” point. This is an example policy with certain rights that can serve as a basis. It is important to emphasize that this policy is only an example and grants users extensive permissions, which may not be desired.
- In the next step, you can add users to this group. Since we will create the user in Step 5, click on “Create group” here.
For more information on individual AWS permissions, refer to the official AWS documentation: AWS User and role policy examples.
Warning
The example policy grants users comprehensive access rights to S3 resources. Before applying this policy, please ensure that you limit your users’ rights to the necessary minimum to ensure the security and protection of your data.The example policy for ransomware mitigation can serve as a starting point. Remember to grant permissions selectively and regularly review them to ensure the integrity of your data.
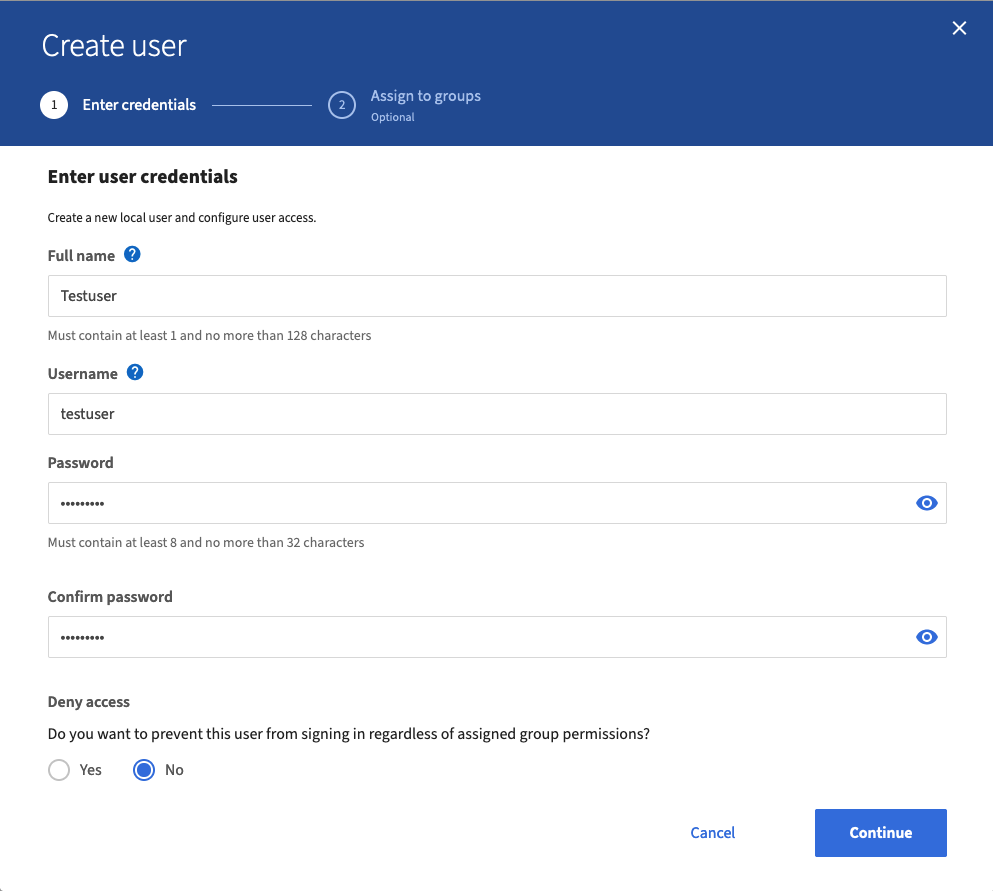
Step 5: Creating Another User
- Select “Users” on the left under “Access Management.” Click on “Create user.”
- Enter the full name of the user in the respective field.
- Assign a desired username that will be used for login later.
- Set a secure password for the user.
- Leave the “Deny access” option set to “No” (This option allows denying access to a user later if necessary.)
- Click on “Continue” to proceed.
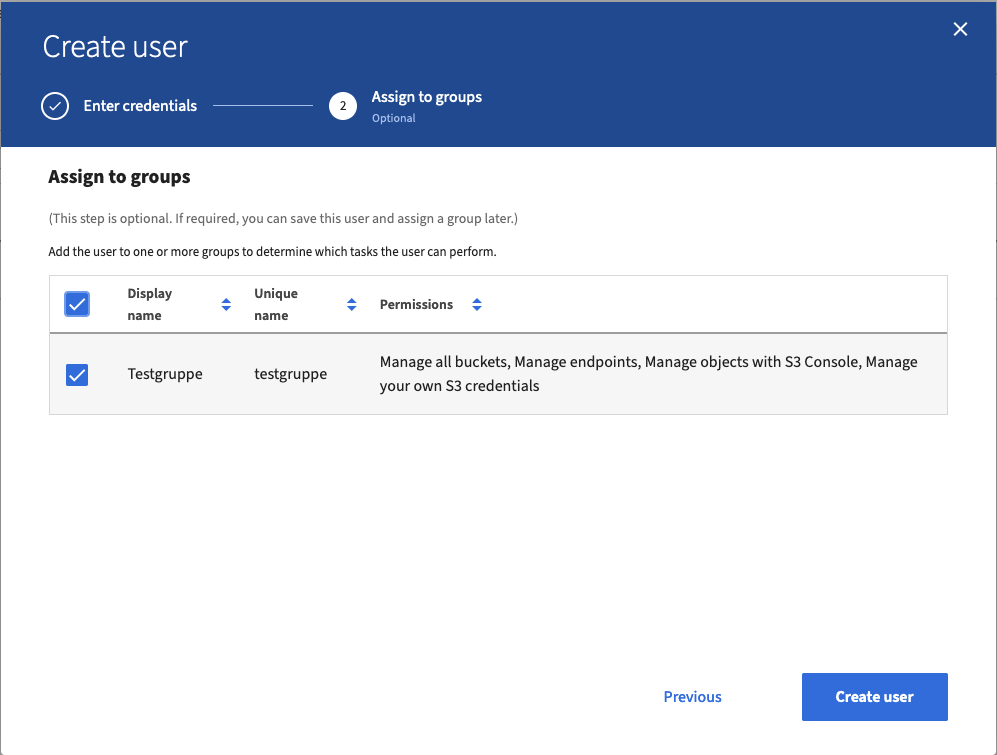
- On the next input screen, you can select the group you created earlier.
- By assigning this group, the user automatically receives the permissions you defined for this group. Click “Create user” to complete.
Step 6: Logging in as the User
- Log in either with the login details of the newly created user or use the root user to edit the user.
Step 7: Generating an Access Key
- After successful login, you have the option to generate an access key.
- An access key is a combination of an access key ID and a secret access key. You need these credentials to access your resources with the AWS S3 Command Line Interface (CLI) or other compatible tools.
- Select “Storage (S3)” on the left and choose “My access keys.”
- Click on the “Create Key” button to create a new access key.
- On the first screen, you have the option to set an endpoint (expiration time) for the access key. This means the access key will become invalid after this time. Alternatively, you can set it to “unlimited” to not restrict its validity.
- After configuration, the access key and secret access key will be displayed. The secret access key is displayed only once. We strongly recommend storing the secret key carefully and protecting it from unauthorized access.
- Alternatively, you can also choose to download the credentials in CSV format. This allows you to store and manage the credentials.