Granting Access to S3 Bucket for a Specific User
2 minute read
In this section, you will learn how to configure an S3 bucket to grant access to only a specific user. This allows you to refine access control at a granular level, restricting access to the bucket to a particular user.
Step 1: Prepare the Information
To create a policy of this kind, you need a set of information:
| Variable | Explanation | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
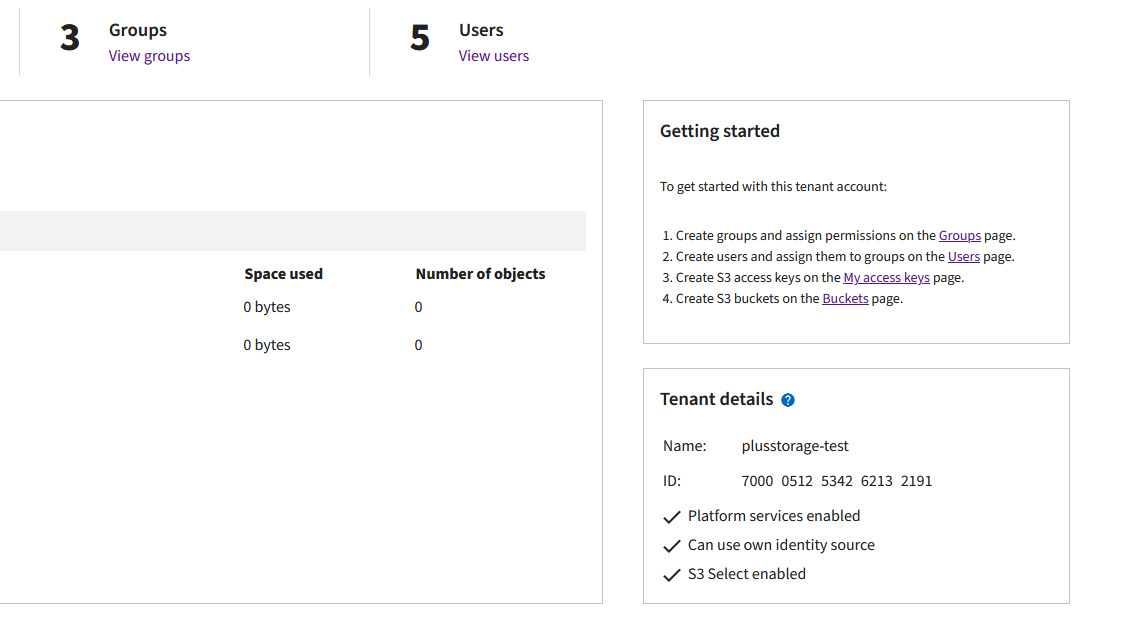
| ACCOUNT_ID | The account ID you used to sign in to the S3 User Portal. You can find this on the dashboard (see Screenshot). | 700001145864652591 |
| BUCKET_NAME | The name of the bucket whose access is regulated by this policy. | examplebucket |
| USERNAME | The username of the specific user for whom a granular access policy will be created. | mmustermann |
Step 2: Create the Bucket Policy
Policies are typically defined using .json objects. In this case, create a user-policy.json file and replace the corresponding variables with the information collected in the last step.
user-policy.json:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Id": "UserBucketPolicy",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowUserAccess",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::ACCOUNT_ID:user/USERNAME"
},
"Action": "s3:*",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::BUCKET_NAME",
"arn:aws:s3:::BUCKET_NAME/*"
]
},
{
"Sid": "DenyOtherAccess",
"Effect": "Deny",
"NotPrincipal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::ACCOUNT_ID:user/USERNAME"
},
"Action": "s3:*",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::BUCKET_NAME",
"arn:aws:s3:::BUCKET_NAME/*"
]
}
]
}
In this specific example, the policy would be as follows:
user-policy.json
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Id": "UserBucketPolicy",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowUserAccess",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::700001145864652591:user/mmustermann"
},
"Action": "s3:*",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::shop-thumbnails",
"arn:aws:s3:::shop-thumbnails/*"
]
},
{
"Sid": "DenyOtherAccess",
"Effect": "Deny",
"NotPrincipal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::700001145864652591:user/mmustermann"
},
"Action": "s3:*",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::shop-thumbnails",
"arn:aws:s3:::shop-thumbnails/*"
]
}
]
}
Step 3: Set the Bucket Policy
aws s3api put-bucket-policy --bucket <bucketname> --policy file://user-policy.json --endpoint-url=https://<endpoint-url>
Explanation of variables:
- <bucketname>: The name of the bucket whose policy you want to check.
- <policy-name>: The name of the policy file you created.
- <endpoint-url>: The corresponding endpoint for your plusserver S3-service.
Example:
aws s3api put-bucket-policy --bucket shop-thumbnails --policy file://user-policy.json --endpoint-url=https://s3.de-west-1.psmanaged.com
Step 4: Check the Bucket Policy
Use the command aws s3api get-bucket-policy to verify that the desired policy has been set:
aws s3api get-bucket-policy --bucket <bucketname> --endpoint-url=https://<endpoint-url>
Explanation of variables:
- <bucketname>: The name of the bucket whose policy you want to check.
- <endpoint-url>: The corresponding endpoint for your plusserver S3 service.
Example:
aws s3api get-bucket-policy --bucket shop-thumbnails --endpoint-url=https://s3.de-west-1.psmanaged.com
After running this command, the output should match the policy you defined and ideally be identical.